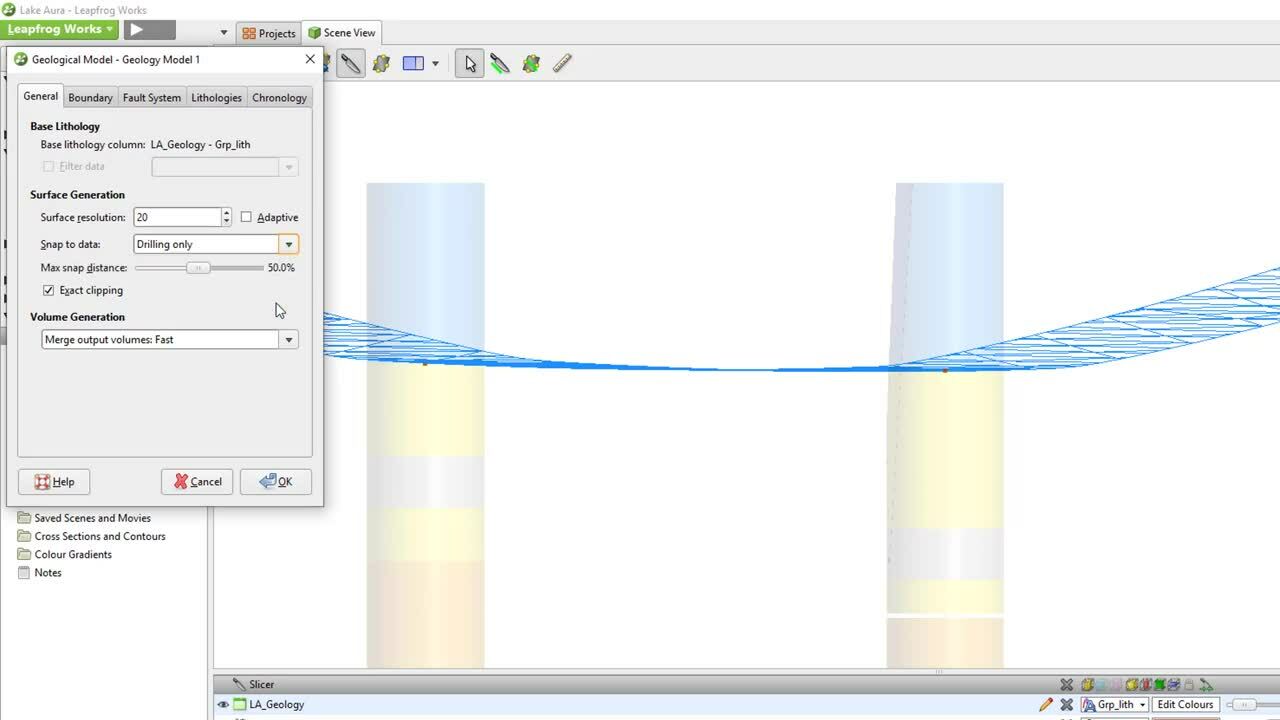
In this video, we will begin to build surfaces representing the different units within the geological model.
Please note: In late 2020, Leapfrog Works received a significant update to its user interface. While the current version of Leapfrog looks quite different from the version used to record this video, most of this content is still valid as the layout, location of functions, and workflows remain largely the same. For more information about the latest new features, please see the Leapfrog Works product page (https://my.seequent.com/products/leapfrog-works/latest).
0:00 – Recap of the previous 3 videos
0:28 – Overview of the geological modelling process in Leapfrog
1:20 – 3 Tips for surface building
2:20 – Introduction to the 4 main surface types
2:36 – Using the Erosion surface type
3:36 – Reviewing a newly built surface
3:55 – Snapping surfaces to boreholes
5:27 – Using the Vein surface type
6:06 – Using the Intrusion surface type
6:24 – Importance of ignoring units when creating contact surfaces – avoid duplicating contact points
7:15 – Using the Deposit surface type
8:17 – Review of contact surfaces
8:41 – Introduction to activating surface to create volumes
8:49 – How to define the Surface Chronology
9:05 – How the Surface Chronology works
9:55 – Re-ordering the surfaces
10:24 – Activating the surfaces to create volumes
10:28 – Discussion of Background Lithology
11:00 – Discussion of volume generation in a Geological Model (GM)
11:22 – Reviewing the volumes in the scene
Duration
12 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Leapfrog Works
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here