O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
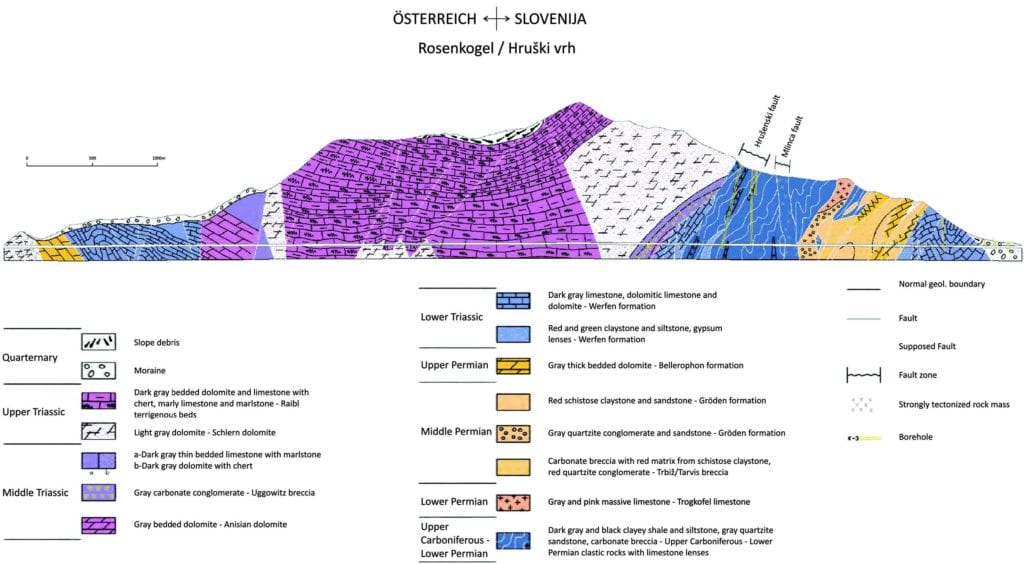
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.
Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
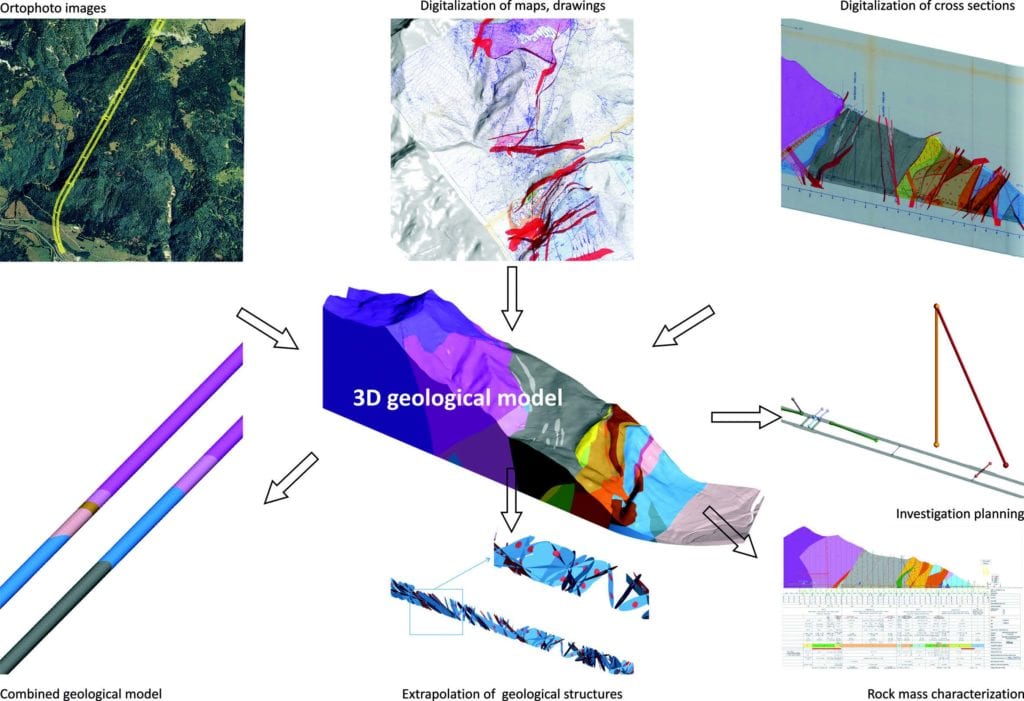
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea
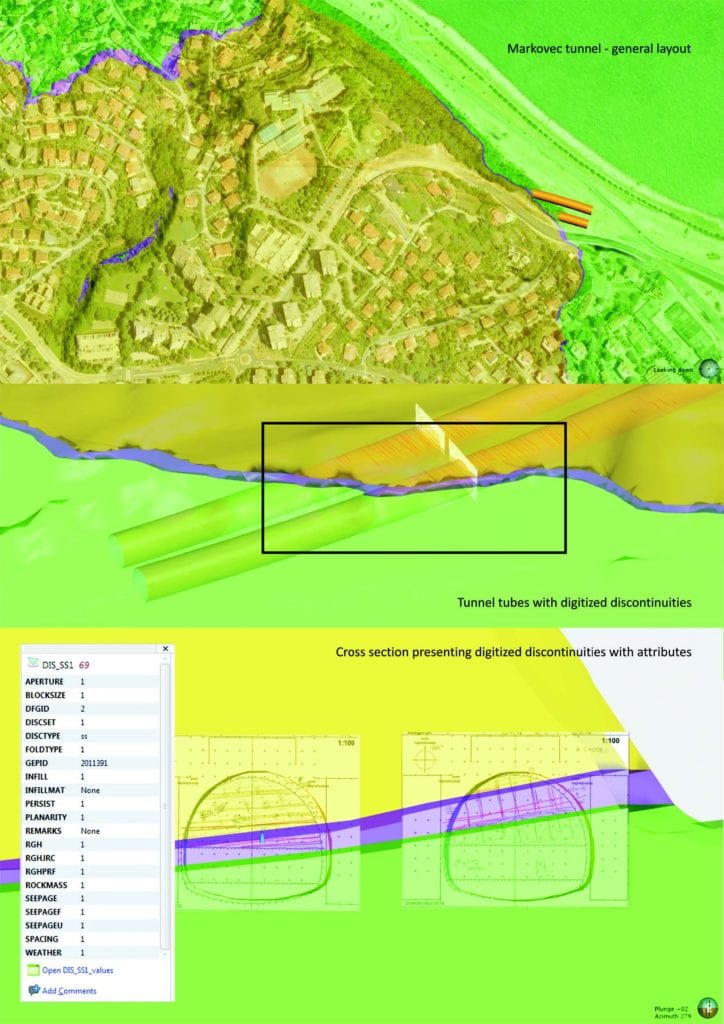
Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.
Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Resposta
Definição da estrutura geológica ao longo do túnel
O modelo em 3D foi criado com base no grande volume de dados geológicos obtidos nos levantamentos anteriores e nas fases de construção, e atualizados após novas descobertas. O modelo único usou todos os registros de testemunhos de sondagem, mapas de frentes de lavra e medições.
Segundo Tina Zivec, “com a grande experiência interdisciplinar da equipe de desenvolvimento e suporte da Seequent, o problema que estávamos enfrentando foi rapidamente compreendido após a criação de um modelo para as disciplinas mais desafiadoras.”
Devido à falta de dados de furos de sondagem, o modelo foi criado com base na determinação do sistema de falhas. As principais falhas foram definidas como polilinhas do GIS e alinhadas em relação à topografia. Em seguida, os dados das falhas que foram modelados e os dados estruturais relacionados a afloramentos foram corrigidos nas seções transversais geológicas ao longo do alinhamento do túnel.
Os dados estruturais obtidos de perfis geológicos detalhados, baseados nos registros de frentes de geologia realizados durante a fase de escavação, foram usados para orientar planos de falhas no nível do túnel.
O sistema de falhas gerado cortou o modelo em 3D em vários blocos de falhas. As unidades litoestratigráficas adequadas foram atribuídas a cada bloco. As propriedades litológicas e estruturais foram extraídas do modelo em 3D criado para criar perfis geológicos detalhados, além de um modelo estrutural para extrapolação das propriedades estruturais para o túnel planejado como uma rede discreta de fraturas (DFN, Discrete Fracture Network).
Com o modelo em 3D, os usuários puderam prever a posição e a orientação dos principais sistemas de falhas, as condições gerais do solo e o comportamento dos maciços rochosos, o que ajudou no desenvolvimento do projeto de tipos de suporte para construção do novo túnel.
Gerenciamento de informações
Além de ter ajudado significativamente no projeto do novo túnel, o Leapfrog Works também permitiu a sinergia com processos de BIM. Um modelo criado no Leapfrog Works é essencialmente um modelo de informações criado com base em diferentes padrões.
O Leapfrog Works é um software rápido, avançado e muito fácil de usar, com boa resolução gráfica, cálculos rápidos e recurso interdisciplinar que permite incluir diferentes estruturas.
Tina Zivec, geóloga, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Resposta
Definição da estrutura geológica ao longo do túnel
O modelo em 3D foi criado com base no grande volume de dados geológicos obtidos nos levantamentos anteriores e nas fases de construção, e atualizados após novas descobertas. O modelo único usou todos os registros de testemunhos de sondagem, mapas de frentes de lavra e medições.
Segundo Tina Zivec, “com a grande experiência interdisciplinar da equipe de desenvolvimento e suporte da Seequent, o problema que estávamos enfrentando foi rapidamente compreendido após a criação de um modelo para as disciplinas mais desafiadoras.”
Devido à falta de dados de furos de sondagem, o modelo foi criado com base na determinação do sistema de falhas. As principais falhas foram definidas como polilinhas do GIS e alinhadas em relação à topografia. Em seguida, os dados das falhas que foram modelados e os dados estruturais relacionados a afloramentos foram corrigidos nas seções transversais geológicas ao longo do alinhamento do túnel.
Os dados estruturais obtidos de perfis geológicos detalhados, baseados nos registros de frentes de geologia realizados durante a fase de escavação, foram usados para orientar planos de falhas no nível do túnel.
O sistema de falhas gerado cortou o modelo em 3D em vários blocos de falhas. As unidades litoestratigráficas adequadas foram atribuídas a cada bloco. As propriedades litológicas e estruturais foram extraídas do modelo em 3D criado para criar perfis geológicos detalhados, além de um modelo estrutural para extrapolação das propriedades estruturais para o túnel planejado como uma rede discreta de fraturas (DFN, Discrete Fracture Network).
Com o modelo em 3D, os usuários puderam prever a posição e a orientação dos principais sistemas de falhas, as condições gerais do solo e o comportamento dos maciços rochosos, o que ajudou no desenvolvimento do projeto de tipos de suporte para construção do novo túnel.
Gerenciamento de informações
Além de ter ajudado significativamente no projeto do novo túnel, o Leapfrog Works também permitiu a sinergia com processos de BIM. Um modelo criado no Leapfrog Works é essencialmente um modelo de informações criado com base em diferentes padrões.
O Leapfrog Works é um software rápido, avançado e muito fácil de usar, com boa resolução gráfica, cálculos rápidos e recurso interdisciplinar que permite incluir diferentes estruturas.
Tina Zivec, geóloga, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Resposta
Definição da estrutura geológica ao longo do túnel
O modelo em 3D foi criado com base no grande volume de dados geológicos obtidos nos levantamentos anteriores e nas fases de construção, e atualizados após novas descobertas. O modelo único usou todos os registros de testemunhos de sondagem, mapas de frentes de lavra e medições.
Segundo Tina Zivec, “com a grande experiência interdisciplinar da equipe de desenvolvimento e suporte da Seequent, o problema que estávamos enfrentando foi rapidamente compreendido após a criação de um modelo para as disciplinas mais desafiadoras.”
Devido à falta de dados de furos de sondagem, o modelo foi criado com base na determinação do sistema de falhas. As principais falhas foram definidas como polilinhas do GIS e alinhadas em relação à topografia. Em seguida, os dados das falhas que foram modelados e os dados estruturais relacionados a afloramentos foram corrigidos nas seções transversais geológicas ao longo do alinhamento do túnel.
Os dados estruturais obtidos de perfis geológicos detalhados, baseados nos registros de frentes de geologia realizados durante a fase de escavação, foram usados para orientar planos de falhas no nível do túnel.
O sistema de falhas gerado cortou o modelo em 3D em vários blocos de falhas. As unidades litoestratigráficas adequadas foram atribuídas a cada bloco. As propriedades litológicas e estruturais foram extraídas do modelo em 3D criado para criar perfis geológicos detalhados, além de um modelo estrutural para extrapolação das propriedades estruturais para o túnel planejado como uma rede discreta de fraturas (DFN, Discrete Fracture Network).
Com o modelo em 3D, os usuários puderam prever a posição e a orientação dos principais sistemas de falhas, as condições gerais do solo e o comportamento dos maciços rochosos, o que ajudou no desenvolvimento do projeto de tipos de suporte para construção do novo túnel.
Gerenciamento de informações
Além de ter ajudado significativamente no projeto do novo túnel, o Leapfrog Works também permitiu a sinergia com processos de BIM. Um modelo criado no Leapfrog Works é essencialmente um modelo de informações criado com base em diferentes padrões.
O Leapfrog Works é um software rápido, avançado e muito fácil de usar, com boa resolução gráfica, cálculos rápidos e recurso interdisciplinar que permite incluir diferentes estruturas.
Tina Zivec, geóloga, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Após a aprovação do projeto, foi criado um modelo de informações de construção (BIM, Building Information Modelling) preliminar completo. Devido às diferentes tecnologias usadas para criar modelos de BIM e do Leapfrog, esses não puderam ser integrados em um ambiente comum sem perda informações. No entanto, a transformação da geometria do túnel no Leapfrog Works permitiu a extração de vários modelos combinados para prever, com precisão, o volume, a distribuição e a quantidade de cada tipo de solo a ser escavado, além da identificação de interseções de descontinuidades estruturais significativas no local. A visualização ajudou a definir o programa de levantamentos e muito mais. As informações e as imagens gráficas extraídas do modelo do Leapfrog Works foram usadas para definir a distribuição de suportes ao longo do túnel. Elas foram usadas como base para gerar uma mesh discretizada para cálculos de elementos finitos.
Resultado final
O uso do Leapfrog Works no projeto de construção do túnel permitiu visualizar facilmente as condições do solo com base em dados de entrada não ambíguos. Esses dados poderiam ser usados para futuros cálculos, avaliações de estabilidade e análises do potencial de deformação. Os benefícios de usar o software incluíram:
- Combinação fácil e rápida de diferentes tipos de dados – com o Leapfrog Works, os modeladores puderam usar tipos de dados complexos e variados obtidos de estudos no escritório e também de levantamentos no local.
- Visualização e compreensão com rapidez – avaliar a viabilidade, identificar discordâncias entre diferentes modelos, verificar especificações, planejar e avaliar custos simultaneamente em diferentes visualizações garante muito mais controle durante o desenvolvimento do projeto do que a verificação de desenhos em PDF, planilhas de cronogramas, especificações e faturas de quantidades. Essas vantagens são aumentadas durante a construção quando alterações podem ser avaliadas quase em tempo real e facilmente registradas com informações de aprovação.
- Acesso à mais avançada modelagem de dados geológicos – o Leapfrog Works é uma avançada ferramenta de modelagem de dados geológico específica para modelar falhas, intrusões e depósitos.
- Simplificação de um processo de refinamento – os modeladores são capazes de incluir novas informações com facilidade. A complexidade da estrutura geológica foi monitorada durante a escavação do túnel existente porque as condições geológicas mudavam em pequenos intervalos de distância. O registro diário das frentes de geologia e o monitoramento dos aspectos geotécnicos e de levantamentos foram incorporados ao modelo. Esse processo pode continuar durante a construção do segundo túnel.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Resposta
Definição da estrutura geológica ao longo do túnel
O modelo em 3D foi criado com base no grande volume de dados geológicos obtidos nos levantamentos anteriores e nas fases de construção, e atualizados após novas descobertas. O modelo único usou todos os registros de testemunhos de sondagem, mapas de frentes de lavra e medições.
Segundo Tina Zivec, “com a grande experiência interdisciplinar da equipe de desenvolvimento e suporte da Seequent, o problema que estávamos enfrentando foi rapidamente compreendido após a criação de um modelo para as disciplinas mais desafiadoras.”
Devido à falta de dados de furos de sondagem, o modelo foi criado com base na determinação do sistema de falhas. As principais falhas foram definidas como polilinhas do GIS e alinhadas em relação à topografia. Em seguida, os dados das falhas que foram modelados e os dados estruturais relacionados a afloramentos foram corrigidos nas seções transversais geológicas ao longo do alinhamento do túnel.
Os dados estruturais obtidos de perfis geológicos detalhados, baseados nos registros de frentes de geologia realizados durante a fase de escavação, foram usados para orientar planos de falhas no nível do túnel.
O sistema de falhas gerado cortou o modelo em 3D em vários blocos de falhas. As unidades litoestratigráficas adequadas foram atribuídas a cada bloco. As propriedades litológicas e estruturais foram extraídas do modelo em 3D criado para criar perfis geológicos detalhados, além de um modelo estrutural para extrapolação das propriedades estruturais para o túnel planejado como uma rede discreta de fraturas (DFN, Discrete Fracture Network).
Com o modelo em 3D, os usuários puderam prever a posição e a orientação dos principais sistemas de falhas, as condições gerais do solo e o comportamento dos maciços rochosos, o que ajudou no desenvolvimento do projeto de tipos de suporte para construção do novo túnel.
Gerenciamento de informações
Além de ter ajudado significativamente no projeto do novo túnel, o Leapfrog Works também permitiu a sinergia com processos de BIM. Um modelo criado no Leapfrog Works é essencialmente um modelo de informações criado com base em diferentes padrões.
O Leapfrog Works é um software rápido, avançado e muito fácil de usar, com boa resolução gráfica, cálculos rápidos e recurso interdisciplinar que permite incluir diferentes estruturas.
Tina Zivec, geóloga, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent’s civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Resposta
Definição da estrutura geológica ao longo do túnel
O modelo em 3D foi criado com base no grande volume de dados geológicos obtidos nos levantamentos anteriores e nas fases de construção, e atualizados após novas descobertas. O modelo único usou todos os registros de testemunhos de sondagem, mapas de frentes de lavra e medições.
Segundo Tina Zivec, “com a grande experiência interdisciplinar da equipe de desenvolvimento e suporte da Seequent, o problema que estávamos enfrentando foi rapidamente compreendido após a criação de um modelo para as disciplinas mais desafiadoras.”
Devido à falta de dados de furos de sondagem, o modelo foi criado com base na determinação do sistema de falhas. As principais falhas foram definidas como polilinhas do GIS e alinhadas em relação à topografia. Em seguida, os dados das falhas que foram modelados e os dados estruturais relacionados a afloramentos foram corrigidos nas seções transversais geológicas ao longo do alinhamento do túnel.
Os dados estruturais obtidos de perfis geológicos detalhados, baseados nos registros de frentes de geologia realizados durante a fase de escavação, foram usados para orientar planos de falhas no nível do túnel.
O sistema de falhas gerado cortou o modelo em 3D em vários blocos de falhas. As unidades litoestratigráficas adequadas foram atribuídas a cada bloco. As propriedades litológicas e estruturais foram extraídas do modelo em 3D criado para criar perfis geológicos detalhados, além de um modelo estrutural para extrapolação das propriedades estruturais para o túnel planejado como uma rede discreta de fraturas (DFN, Discrete Fracture Network).
Com o modelo em 3D, os usuários puderam prever a posição e a orientação dos principais sistemas de falhas, as condições gerais do solo e o comportamento dos maciços rochosos, o que ajudou no desenvolvimento do projeto de tipos de suporte para construção do novo túnel.
Gerenciamento de informações
Além de ter ajudado significativamente no projeto do novo túnel, o Leapfrog Works também permitiu a sinergia com processos de BIM. Um modelo criado no Leapfrog Works é essencialmente um modelo de informações criado com base em diferentes padrões.
O Leapfrog Works é um software rápido, avançado e muito fácil de usar, com boa resolução gráfica, cálculos rápidos e recurso interdisciplinar que permite incluir diferentes estruturas.
Tina Zivec, geóloga, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Após a aprovação do projeto, foi criado um modelo de informações de construção (BIM, Building Information Modelling) preliminar completo. Devido às diferentes tecnologias usadas para criar modelos de BIM e do Leapfrog, esses não puderam ser integrados em um ambiente comum sem perda informações. No entanto, a transformação da geometria do túnel no Leapfrog Works permitiu a extração de vários modelos combinados para prever, com precisão, o volume, a distribuição e a quantidade de cada tipo de solo a ser escavado, além da identificação de interseções de descontinuidades estruturais significativas no local. A visualização ajudou a definir o programa de levantamentos e muito mais. As informações e as imagens gráficas extraídas do modelo do Leapfrog Works foram usadas para definir a distribuição de suportes ao longo do túnel. Elas foram usadas como base para gerar uma mesh discretizada para cálculos de elementos finitos.
Resultado final
O uso do Leapfrog Works no projeto de construção do túnel permitiu visualizar facilmente as condições do solo com base em dados de entrada não ambíguos. Esses dados poderiam ser usados para futuros cálculos, avaliações de estabilidade e análises do potencial de deformação. Os benefícios de usar o software incluíram:
- Combinação fácil e rápida de diferentes tipos de dados – com o Leapfrog Works, os modeladores puderam usar tipos de dados complexos e variados obtidos de estudos no escritório e também de levantamentos no local.
- Visualização e compreensão com rapidez – avaliar a viabilidade, identificar discordâncias entre diferentes modelos, verificar especificações, planejar e avaliar custos simultaneamente em diferentes visualizações garante muito mais controle durante o desenvolvimento do projeto do que a verificação de desenhos em PDF, planilhas de cronogramas, especificações e faturas de quantidades. Essas vantagens são aumentadas durante a construção quando alterações podem ser avaliadas quase em tempo real e facilmente registradas com informações de aprovação.
- Acesso à mais avançada modelagem de dados geológicos – o Leapfrog Works é uma avançada ferramenta de modelagem de dados geológico específica para modelar falhas, intrusões e depósitos.
- Simplificação de um processo de refinamento – os modeladores são capazes de incluir novas informações com facilidade. A complexidade da estrutura geológica foi monitorada durante a escavação do túnel existente porque as condições geológicas mudavam em pequenos intervalos de distância. O registro diário das frentes de geologia e o monitoramento dos aspectos geotécnicos e de levantamentos foram incorporados ao modelo. Esse processo pode continuar durante a construção do segundo túnel.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Resposta
Definição da estrutura geológica ao longo do túnel
O modelo em 3D foi criado com base no grande volume de dados geológicos obtidos nos levantamentos anteriores e nas fases de construção, e atualizados após novas descobertas. O modelo único usou todos os registros de testemunhos de sondagem, mapas de frentes de lavra e medições.
Segundo Tina Zivec, “com a grande experiência interdisciplinar da equipe de desenvolvimento e suporte da Seequent, o problema que estávamos enfrentando foi rapidamente compreendido após a criação de um modelo para as disciplinas mais desafiadoras.”
Devido à falta de dados de furos de sondagem, o modelo foi criado com base na determinação do sistema de falhas. As principais falhas foram definidas como polilinhas do GIS e alinhadas em relação à topografia. Em seguida, os dados das falhas que foram modelados e os dados estruturais relacionados a afloramentos foram corrigidos nas seções transversais geológicas ao longo do alinhamento do túnel.
Os dados estruturais obtidos de perfis geológicos detalhados, baseados nos registros de frentes de geologia realizados durante a fase de escavação, foram usados para orientar planos de falhas no nível do túnel.
O sistema de falhas gerado cortou o modelo em 3D em vários blocos de falhas. As unidades litoestratigráficas adequadas foram atribuídas a cada bloco. As propriedades litológicas e estruturais foram extraídas do modelo em 3D criado para criar perfis geológicos detalhados, além de um modelo estrutural para extrapolação das propriedades estruturais para o túnel planejado como uma rede discreta de fraturas (DFN, Discrete Fracture Network).
Com o modelo em 3D, os usuários puderam prever a posição e a orientação dos principais sistemas de falhas, as condições gerais do solo e o comportamento dos maciços rochosos, o que ajudou no desenvolvimento do projeto de tipos de suporte para construção do novo túnel.
Gerenciamento de informações
Além de ter ajudado significativamente no projeto do novo túnel, o Leapfrog Works também permitiu a sinergia com processos de BIM. Um modelo criado no Leapfrog Works é essencialmente um modelo de informações criado com base em diferentes padrões.
O Leapfrog Works é um software rápido, avançado e muito fácil de usar, com boa resolução gráfica, cálculos rápidos e recurso interdisciplinar que permite incluir diferentes estruturas.
Tina Zivec, geóloga, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Projeto do túnel Karasvanke da Elea iC (Eslovênia)
O projeto
O túnel Karavanke, construído na década de 1980, corta os Alpes entre a Eslovênia e a Áustria, e representa um ponto crítico no Corredor X de transporte pan-europeu. A necessidade de melhorar o tráfego e a segurança na estrada levou, em 2013, ao planejamento de um segundo túnel.
O projeto do segundo túnel envolve a construção de um túnel de 7.820 metros de extensão com duas pistas e capeamento de solo até 1.000 metros. A geologia é muito complexa devido à sua estrutura de leques imbricados, que se formou como um arranjo de dobras sobrepostas de propagação de falhas. No primeiro túnel, foram encontradas condições geológicas difíceis, como frequentes infiltrações de água, sobrescavações e detecção de metano. Vários levantamentos geológicos, geotécnicos e hidrogeológicos foram realizados desde a década de 1970, e os dados geraram abrangente documentação sobre o projeto.
A empresa de consultoria interdisciplinar Elea iC, que é parceira líder da joint venture Karavanke, usou o Leapfrog Works para modelar os dados de geologia como parte do projeto Idea Phase para a parte eslovena do segundo túnel.
Situação
Tradicionalmente, a modelagem geológica em 3D no setor de construção civil tem se limitado à interpretações em 2D em um ambiente em 3D. Esse processo é muito lento, e inclui perda de informações entre seções transversais, interpretações subjetivas das condições geológicas e avaliação de potenciais riscos. Além disso, o processo de atualização das interpretações manuais em 2D não é simples, o que aumenta os riscos. O projeto do túnel Karavanke e um amplo conjunto de dados do projeto deram à Elea iC a oportunidade de testar tecnologias emergentes e melhorar a qualidade da geologia de engenharia, da geotecnia e da construção de túneis.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types – Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding – Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling – Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement – Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here





