После утверждения проекта изготовлена полная предварительная BIM-модель тоннеля. Так как в основе информационного моделирования объектов (BIM) и модели Leapfrog лежали различные технологии, модели нельзя было интегрировать в общую среду без потери некоторой информации. Тем не менее, преобразованная геометрия тоннеля в Leapfrog Works позволила извлечь несколько различных комбинированных моделей для точного прогнозирования объемов выемки, распределения и количества каждого типа грунта и выявления критических пересекающихся структурных нарушений сплошности. Визуализация помогла определить программу исследований и многое другое. Информация и графика, извлеченные из модели Leapfrog Works, использованы для определения распределения опор вдоль тоннеля. Это послужило основой для создания дискретизированной каркасной сетки для расчетов при помощи метода конечных элементов.
Результат
Использование Leapfrog Works для проекта проходки тоннеля позволило визуализировать грунтовые условия на основе однозначных вводных данных. Эти данные могут быть использованы для дальнейших расчетов, анализа устойчивости и деформационного потенциала. Преимущества использования программного обеспечения:
- Быстрое и легкое комбинирование различных типов данных — Leapfrog Works позволила разработчикам моделей использовать сложные и разнообразные типы данных, собранные как в результате кабинетных исследований, так и исследований на месте.
- Быстрая визуализация и понимание — оценка осуществимости, выявление противоречий между различными моделями, одновременная проверка спецификаций, планирования и калькуляции в разных представлениях обеспечивают гораздо больший контроль над проектом, чем проверка чертежей PDF, расписаний, спецификаций и ведомостей объемов работ. Эти преимущества возрастут во время строительства, когда изменения можно будет оценивать почти в реальном времени и легко регистрировать вместе с информацией об утверждении.
- Доступ к современному геологическому моделированию — Leapfrog Works представляет собой современный специализированный инструмент геологического моделирования, специально разработанный для моделирования разломов, интрузий и месторождений.
- Облегчение процесса уточнения моделей — разработчики моделей могут легко включать в них новую информацию. Сложность геологического строения контролировалась во время выемки грунта из существующей трубы тоннеля, так как геологические условия менялись на небольших расстояниях. В модель включены ежедневный геологический каротаж, инженерно-геологические и изыскательские работы. Этот процесс может продолжаться во время строительства второй трубы тоннеля.
Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea
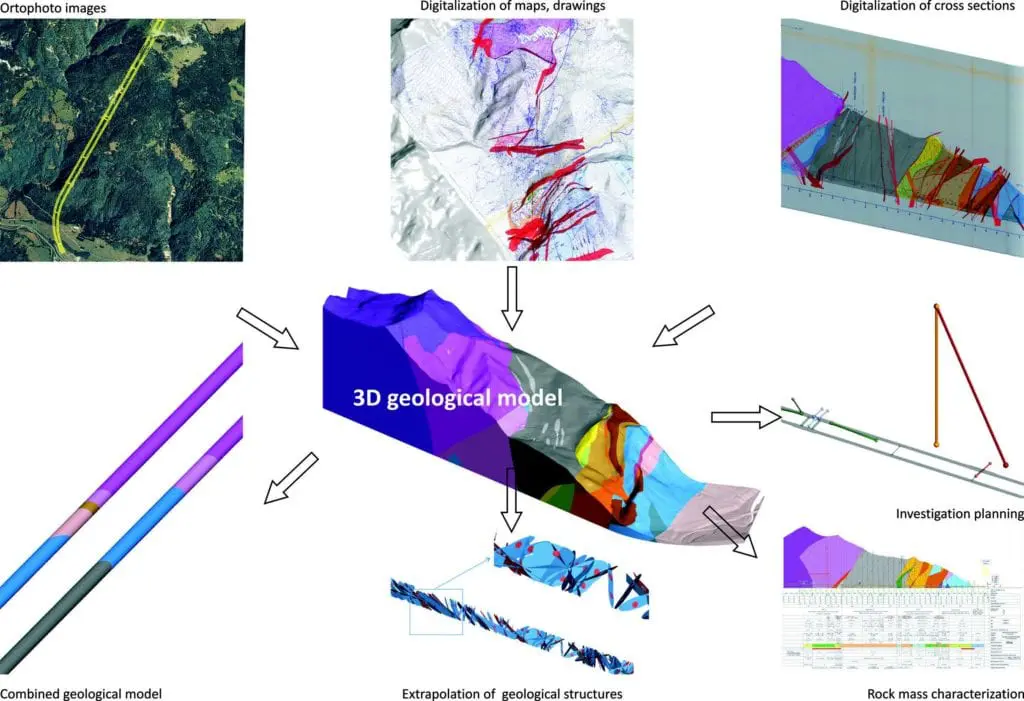
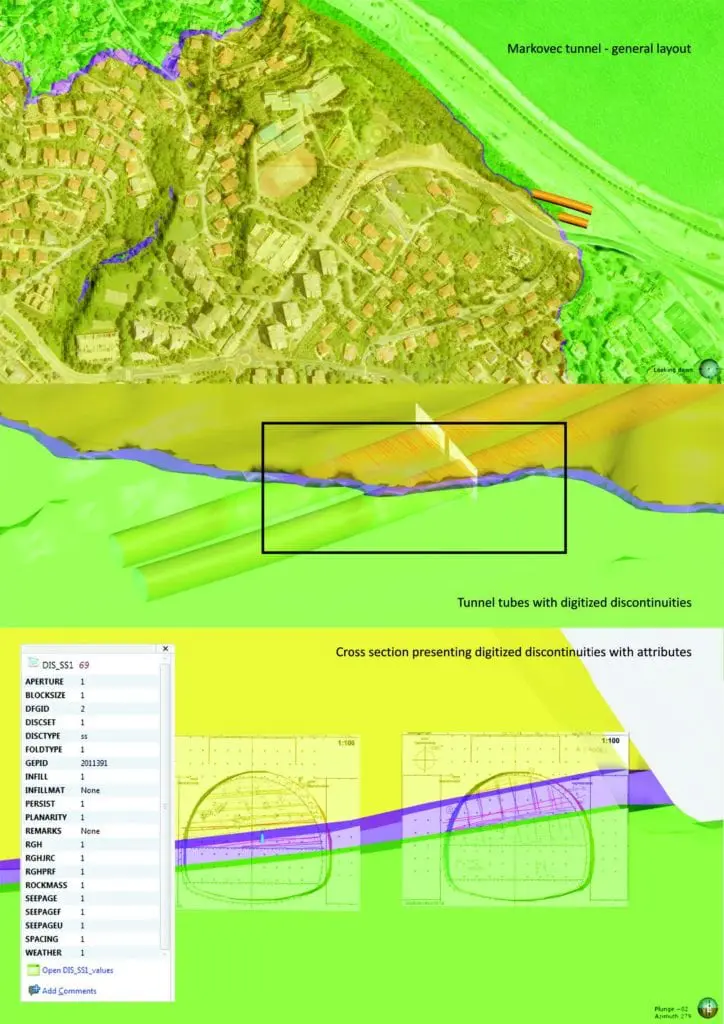
Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types — Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding — Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling — Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement — Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Проект тоннеля Караванке, ELEA IC (Словения)
Проект
Тоннель Караванке, построенный в 1980-х годах, проходит через Альпы между Словенией и Австрией и представляет собой критически важную точку в Общеевропейском транспортном коридоре «X». Потребность в улучшении транспортного потока и повышении безопасности дорожного движения привела в 2013 году к проектированию второй трубы тоннеля.
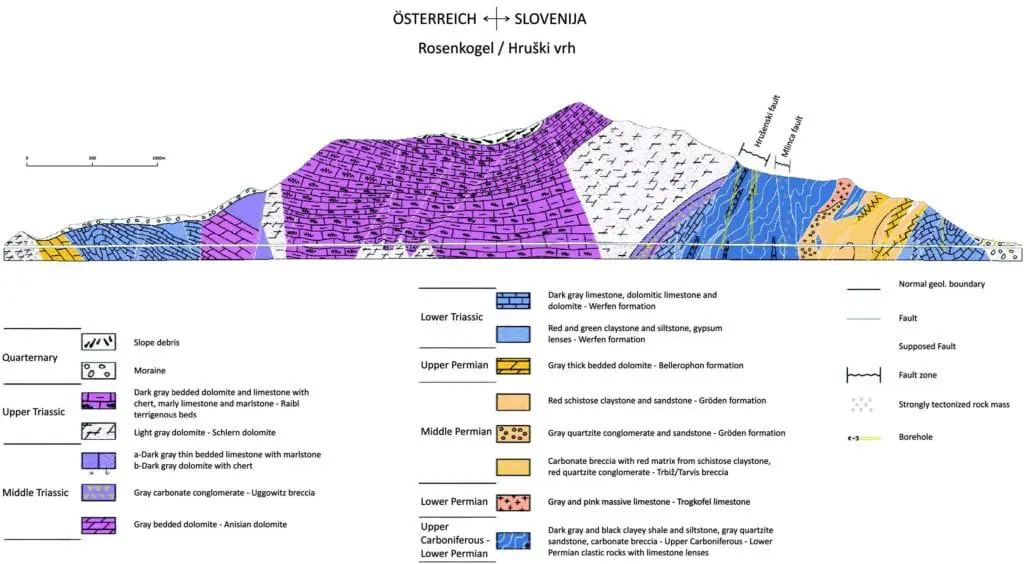
Конструкция второй трубы тоннеля представляет собой двухполосный тоннель длиной 7820 м с мощностью покрывающей породы до 1000 м. Геологическое строение очень сложно ввиду кулисной веерной структуры, которая сформировалась как массив перекрывающихся складок распространения разломов. Первоначальный тоннель столкнулся с трудными геологическими условиями с частым сильным притоком воды, прорывами и обнаружением метана. В результате серии геологических, инженерно-геологических и гидрогеологических исследований, проведенных с 1970-х годов, набран большой объем проектной документации.
Междисциплинарная консалтинговая компания Elea iC, ведущий партнер совместного предприятия «Караванке», использовала Leapfrog Works для моделирования геологического строения в рамках проекта Idea Phase для словенской части второй трубы тоннеля.
Исходные условия
Традиционно трехмерное геологическое моделирование в гражданской промышленности ограничивалось двумерной интерпретацией в трехмерной среде. Этот процесс занимает много времени, с потерей информации между секциями и субъективной интерпретацией геологических условий и оценкой потенциальных рисков. Созданные вручную двумерные интерпретации также сложно обновлять, что увеличивает риск. Проект тоннеля Караванке и обширный набор данных предоставили Elea iC возможность протестировать новые технологии и вывести инженерную геологию, геотехнику и тоннелестроение на новый уровень.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types — Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding — Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling — Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement — Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here

Ответ
Определение геологической структуры вдоль маршрута тоннеля
Трехмерная модель построена на основе обширных геологических данных предыдущих этапов исследования и строительства и дополнена новыми данными. В единой модели использованы все доступные записи, поверхности карты и измерения.
По словам Тины Живец, «обширный межотраслевой опыт команды разработчиков и поддержки Seequent позволил им быстро понять проблему, с которой мы столкнулись при построении модели в самых сложных дисциплинах».
Вследствие отсутствия скважинных данных модель построена путем определения системы разломов. Основные разломы заданы как полилинии ГИС и выровнены по топографии. Затем смоделированные разломы и структурные данные выходов пластов на поверхность скорректированы до геологических разрезов вдоль трассы тоннеля.
Структурные данные из подробных геологических профилей, основанные на геологическом каротажном исследовании на этапе выемки грунта, использовались для ориентирования плоскостей разломов на уровне тоннеля.
Созданная система разломов разрезала трехмерную модель на многочисленные ограниченные разломами блоки. Каждому блоку присвоены соответствующие литостратиграфические комплексы. Из полученной трехмерной модели извлечены литологические и структурные свойства для создания подробных геологических профилей, а также структурная модель для экстраполяции структурных свойств на проектируемую трубу тоннеля в виде дискретной сети трещин (DFN).
Трехмерная модель позволила пользователям прогнозировать местоположение и ориентацию основных систем разломов, общие грунтовые условия и поведение массива пород, а также помогла проектировать типы опор для строительства новой трубы тоннеля.
Управление информацией
В дополнение к значительной помощи в проектировании новой трубы тоннеля Leapfrog Works также обеспечила синергию с процессами информационного моделирования объектов (BIM). Модель Leapfrog Works — это, по сути, информационная модель, построенная в соответствии с различными стандартами.
Leapfrog Works представляет собой быстрое, мощное и удобное программное обеспечение с хорошей графикой, быстрыми вычислениями и междисциплинарными возможностями для включения различных структур.
Тина Живец (Tina Zivec), геолог, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types — Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding — Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling — Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement — Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
Проект тоннеля Караванке, ELEA IC (Словения)
Проект
Тоннель Караванке, построенный в 1980-х годах, проходит через Альпы между Словенией и Австрией и представляет собой критически важную точку в Общеевропейском транспортном коридоре «X». Потребность в улучшении транспортного потока и повышении безопасности дорожного движения привела в 2013 году к проектированию второй трубы тоннеля.
Конструкция второй трубы тоннеля представляет собой двухполосный тоннель длиной 7820 м с мощностью покрывающей породы до 1000 м. Геологическое строение очень сложно ввиду кулисной веерной структуры, которая сформировалась как массив перекрывающихся складок распространения разломов. Первоначальный тоннель столкнулся с трудными геологическими условиями с частым сильным притоком воды, прорывами и обнаружением метана. В результате серии геологических, инженерно-геологических и гидрогеологических исследований, проведенных с 1970-х годов, набран большой объем проектной документации.
Междисциплинарная консалтинговая компания Elea iC, ведущий партнер совместного предприятия «Караванке», использовала Leapfrog Works для моделирования геологического строения в рамках проекта Idea Phase для словенской части второй трубы тоннеля.
Исходные условия
Традиционно трехмерное геологическое моделирование в гражданской промышленности ограничивалось двумерной интерпретацией в трехмерной среде. Этот процесс занимает много времени, с потерей информации между секциями и субъективной интерпретацией геологических условий и оценкой потенциальных рисков. Созданные вручную двумерные интерпретации также сложно обновлять, что увеличивает риск. Проект тоннеля Караванке и обширный набор данных предоставили Elea iC возможность протестировать новые технологии и вывести инженерную геологию, геотехнику и тоннелестроение на новый уровень.

Response
Defining the geological structure along the tunnel tube
The 3D model was built based on the extensive geological data from previous investigation and construction phases, upgraded with new findings. The single model used all available loggings, map faces, and measurements.
Says Tina Zivec, “The extensive interdisciplinary experience of Seequent’s development and support team enabled them to quickly understand the problem we faced with building the model in the most challenging disciplines.”
Due to a lack of borehole data the model was built by determining the fault system. Major faults were determined as GIS polylines and aligned to the topography. Modelled faults and structural data from outcrops were then corrected to geological cross-sections along the tunnel alignment.
Structural data from detailed geological profiles, based on geological face logging during the excavation phase, were used for orienting fault planes in the tunnel level.
The generated fault system cut the 3D model into numerous fault blocks. Appropriate lithostratigraphic units were assigned to each block. From the resulting 3D model, lithological and structural properties were extracted to create detailed geological profiles, as well as a structural model for extrapolating structural properties to the planned tunnel tube as a DFN (Discrete Fracture Network).
The 3D model allowed users to predict the location and orientation of major fault systems, general ground conditions and rock mass behaviour and aided designing support types for constructing the new tunnel tube.
Information Management
In addition to aiding significantly in the design of the new tunnel tube, Leapfrog Works also enabled synergy with BIM processes. A Leapfrog Works model is essentially an information model built under different standards.
Leapfrog Works represents a fast, powerful and user friendly software, with good graphics, fast calculations and interdisciplinary ability for including different structures.
Tina Zivec, Geologist, Elea

Following the design approval, a full preliminary tunnel BIM model was produced. Due to different technology behind BIM and the Leapfrog model, models could not be integrated in a common environment without losing some information. Nevertheless, transformed tunnel geometry in Leapfrog Works allowed the extraction of several different combined models to precisely predict excavation volumes, distribution and quantities of each ground type and the identification of critical intersecting structural discontinuities. Visualisation helped in defining the investigation program and much more. Information and graphics extracted from the Leapfrog Works model were used to define the support distribution along the tunnel. This was used as a basis to generate discretized mesh for Finite-Element calculations.
Outcome
Using Leapfrog Works for the tunnelling project allowed the ready visualisation of ground conditions based on unambiguous input data. This data could be used for further calculations, stability and deformation potential analysis. Benefits of using the software included:
- Fast and easy combining of different data types — Leapfrog Works allowed the modellers to use complex and varied types of data collected from both desk study and in situ investigation.
- Rapid visualisation and understanding — Evaluating feasibility, identifying clashes between different models, checking specifications, scheduling and costings simultaneously in different views gives far more control over design than checking PDF drawings, time schedule sheets, specifications and bills of quantities. These advantages will be enhanced during construction when changes can be evaluated in almost real time and easily recorded along with approval information.
- Access to state of the art geological modelling — Leapfrog Works is an advanced, specialised geological modelling tool specifically designed to model faults, intrusions and deposits.
- Facilitating a process of refinement — Modellers are able to readily incorporate new information. The complexity of the geological structure was monitored during the excavation of the existing tunnel tube, as the geological conditions changed in short distances. Daily geological face logging, geotechnical and surveying monitoring was incorporated into the model. This process can continue during construction of the second tunnel tube.

Duration
2 min

See more on demand videos
VideosFind out more about Seequent's civil solutions
Learn moreVideo Transcript
The video transcript gets copy and pasted here
